前言
为什么需要修改fabric的国密算法?
众所周知的原因,DES和AES等对称加密算法的关键之处:S盒是掌握在美国的手里的,所以是不可信任的。非对称加密算法也有未知的后门,所以我们必须进行替换成国密算法,sm2,sm3和sm4。
密码学算法在fabric的应用场景
常用的密码学分为对称加密,非对称加密和hash算法。
非对称密码学算法主要用在:提案交易,背书交易,创建区块,tls和证书验证中。
| 算法 | 场景 | 算法 | 总结 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 非对称加密 | 提案交易,背书交易,创建区块,tls和证书验证中 | ECDSA,RSA | 提供签名和验签的功能 |
| 对称加密 | 数据进行加密 | AES | 加密业务数据 |
| hash算法 | 签名前进行hash,产生唯一的id,每个区块包含前一个区块的hash | SHA-256,SHA-384,SHA3-256 |
国密算法的介绍
SM是商密算法,不涉及国家秘密。
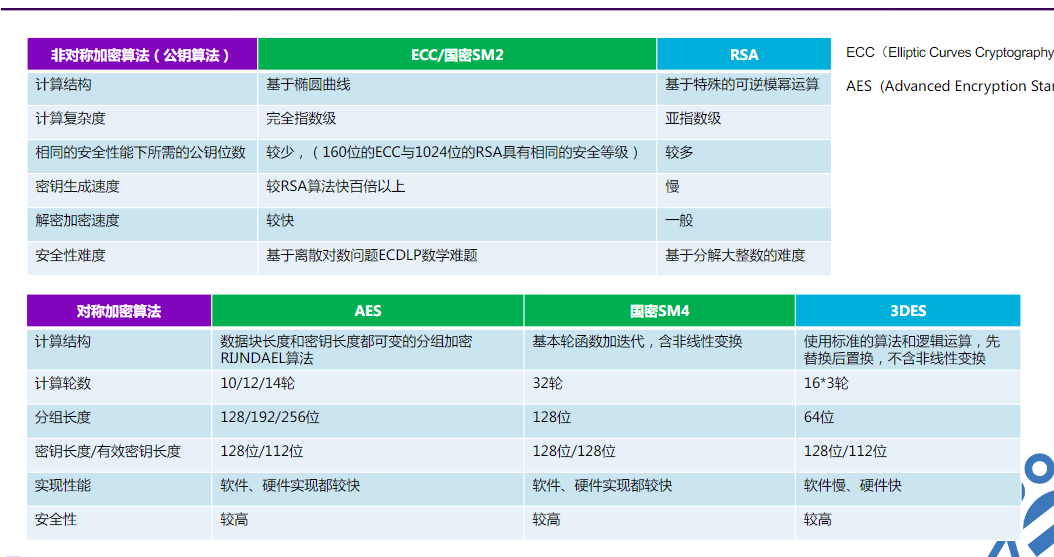
| 非对称密码算法对比 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| sm2 | 基于椭圆曲线密码的公钥,包含数字签名,密钥交换和公钥加密,用于替换RSA/D-H/ESDSA |
| sm3 | 哈希算法,用于替换MD5,SHA-256 |
| sm4 | 对称加密,AES和DES |
1. Hyperledger Fabric 国密补丁的使用
用于Hyperledger Fabric项目支持国密算法,支持V1.1.x以上版本
cryptogen工具配套支持
当前版本采用非插件方式。
上面是刘地军版本的,下面是社区版本。
准备条件
- 可以编译fabric的主机环境,如ubuntu或者osx
- 安装git环境
- 拉取并且切换到所需要的fabric版本
说明:本文是基于fabric release-1.3。
安装步骤
在fabric主目录下,git checkout release-1.3(注意,只能使用正式版本)
-
git clone https://github.com/flyinox/fabric-sm-patch.git
-
git am ./fabric-sm-patch/fabric-sm-patch
-
make [docker native] 使用make编译国密版native或者docker镜像
推荐使用docker镜像方式,其中自带bccsp密码插件
若使用native方式运行,请注意在peer或者orderer启动时,配置config文件中bccsp密码插件的位置(peer对应core.yaml, orderer对应orderer.yaml),更改方式参见下一章节
(注意,当前dep 和 test 跑不过,所以make docker的时候最后会报错,不影响使用)
2. 原理解析
git 可以使用patch来记录我们对代码的修改。
什么是生成patch? 生成patch就是记录你对代码的修改并将其保存在patch文件中。
什么是打patch?打patch就是将patch文件中对代码的修改,应用到源代码,从而把对代码的修改应用到code中。
当我们拿到别人的补丁后,在代码中,执行git am *.patch即可实现补丁的加入。
其实这里还是挺奇怪的,git commit之后,我们可以知道之前的分支的内容,是因为git仓库中的.git文件在追踪,但是patch真的神奇了,是谁在追踪这些具体的变化呢。真是头大,后面再找找原因吧。
补充:找到原因了,具体的修改确实是在patch文件中的,比如:

注意:补丁中的id和打完补丁后的id是不一样的,我的理解是前者是补丁作者提交的id,后者是我们打完补丁后生成的id,二者不是一回事。
2.1 fabric密码服务套件之BCCSP
|– ***opts.go:BCCSP服务可以使用到的各种技术选项 |– bccsp.go |– bccsp_test.go |– factory |– gm:国密 |– keystore.go |– mocks |– opts.go |– pkcs11 |– signer:实现crypto标准库的Signer接口 |– sw `– utils
factory/factory.go中定义的的全局变量保存所有产生的BCCSP的实例。
2.1.1 什么是BCCSP
BCCSP全称是区块链密码服务提供者,用来提供区块链相关的算法标准和他们的实现。
bccsp.go
// BCCSP is the blockchain cryptographic service provider that offers
// the implementation of cryptographic standards and algorithms.
type BCCSP interface {
// KeyGen generates a key using opts.
KeyGen(opts KeyGenOpts) (k Key, err error)
// KeyDeriv derives a key from k using opts.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the primitive used.
KeyDeriv(k Key, opts KeyDerivOpts) (dk Key, err error)
// KeyImport imports a key from its raw representation using opts.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the primitive used.
KeyImport(raw interface{}, opts KeyImportOpts) (k Key, err error)
// GetKey returns the key this CSP associates to
// the Subject Key Identifier ski.
GetKey(ski []byte) (k Key, err error)
// Hash hashes messages msg using options opts.
// If opts is nil, the default hash function will be used.
Hash(msg []byte, opts HashOpts) (hash []byte, err error)
// GetHash returns and instance of hash.Hash using options opts.
// If opts is nil, the default hash function will be returned.
GetHash(opts HashOpts) (h hash.Hash, err error)
// Sign signs digest using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
//
// Note that when a signature of a hash of a larger message is needed,
// the caller is responsible for hashing the larger message and passing
// the hash (as digest).
Sign(k Key, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (signature []byte, err error)
// Verify verifies signature against key k and digest
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Verify(k Key, signature, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (valid bool, err error)
// Encrypt encrypts plaintext using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Encrypt(k Key, plaintext []byte, opts EncrypterOpts) (ciphertext []byte, err error)
// Decrypt decrypts ciphertext using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Decrypt(k Key, ciphertext []byte, opts DecrypterOpts) (plaintext []byte, err error)
}
代码译注
秘钥生命周期管理
- GenKey - 产生秘钥
- DeriveKey -派生秘钥
- GetKey - 获取秘钥
- ImportKey - 导入秘钥
签名验签操作
- Sign -签名
- Verify -验签
加解密操作
- Encrypt - 加密操作
- Decrypt - 解密操作
在opts.go(opts多个选项)定义了所有可用的加密算法。我们重新生成了一个文件sm2opts.go。就是把国外的ECDSA,RSA等替换为sm2,sm3和sm4。我们在fabric目录下使用 grep -r -n "sm2opts.go" .来搜索,发现最终生成的二进制文件使用了sm2opts。
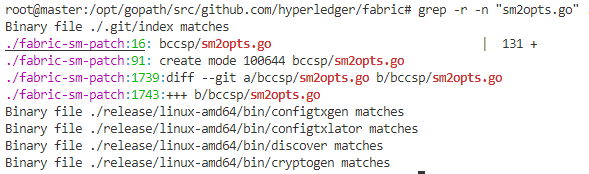
2.1.2 Hyperledger Fabric中BCCSP的整合方式
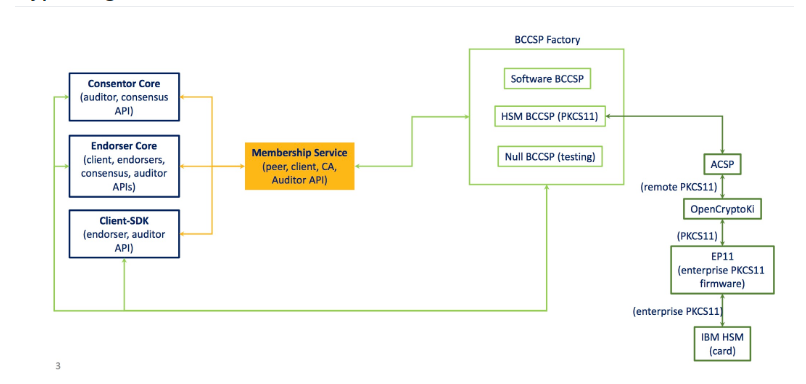
框图译注
BCCSP Factory 主要提供3种BCCSP实现。
- 软件实现 Software BCCSP(使用crypto库)
- 基于PKCS11(Public-key Cryptography Standards)的硬件实现 HSM BCCSP ,HSM即Hardware Security Modules(https://github.com/miekg/pkcs11)
- 测试用的空实现 Null BCCSP (testing)
BCCSP通过Membership Service(成员服务提供者)给相关核心功能和客户端SDK提供加密算法相关的服务。
相关核心功能集中在core中,包括共识模块,背书模块等。
2.1.3 BCCSP设计目标
- 可插拔
- 在不改变核心代码的情况下,可以使用多种加密实现方式
- 提供多种CSP
- 可以添加多种CSP,比如不同的硬件实现
- 允许在不同的模块上面使用不同的CSP
- 支持国际标准
- 通过新的CSP来做支持
- 不需要对不同标准之间的互通做保证
2.1.4 BCCSP秘钥
bccsp.go
// Key represents a cryptographic key
type Key interface {
// Bytes converts this key to its byte representation,
// if this operation is allowed.
Bytes() ([]byte, error)
// SKI returns the subject key identifier of this key.
SKI() []byte
// Symmetric returns true if this key is a symmetric key,
// false is this key is asymmetric
Symmetric() bool
// Private returns true if this key is a private key,
// false otherwise.
Private() bool
// PublicKey returns the corresponding public key part of an asymmetric public/private key pair.
// This method returns an error in symmetric key schemes.
PublicKey() (Key, error)
}
KEY用来对密钥进行抽象和管理,KEY描述了密码相关的秘钥,秘钥可以是对称的或者非对称的。
如果是非对称的,那么秘钥还分为公钥和私钥两种
如果是私钥的话,它还可以通过PublicKey()来获取对应的公钥
秘钥可以通过Subject Key Identifier (GetSKI)来索引。
KeyStore用来进行密钥的存储,因为密钥不能只存储在内存中,必须进行持久化。
2.1.5 秘钥生命周期
为了进行密码相关的操作,需要产生相应的秘钥(译注:并且维护相应的秘钥状态,比如存储,索引)
bccsp.go
GenKey(opts GenKeyOpts) (k Key, err error)
bccsp.go
// KeyGenOpts contains options for key-generation with a CSP.
type KeyGenOpts interface {
// Algorithm returns the key generation algorithm identifier (to be used).
Algorithm() string
// Ephemeral returns true if the key to generate has to be ephemeral,
// false otherwise.
Ephemeral() bool
}
GenKey可以通过不同的opts来控制,产生不同种类的秘钥
对于开发者来说,至少需要为指定生成秘钥的算法和是否是短期秘钥。如果是长期秘钥的话,则需要通过SKI来完成存储和索引
短期秘钥的话,如果没有地方再引用了,会自动被销毁。
值得注意的是,除了这两个方法,其他任何的参数,你都可以在实现此接口GenKeyOpts的时候加上。
有时需要通过已有的秘钥派生新的秘钥
bccsp.go
DeriveKey(k Key, opts DeriveKeyOpts) (dk Key, err error)
bccsp.go
// KeyDerivOpts contains options for key-derivation with a CSP.
type KeyDerivOpts interface {
// Algorithm returns the key derivation algorithm identifier (to be used).
Algorithm() string
// Ephemeral returns true if the key to derived has to be ephemeral,
// false otherwise.
Ephemeral() bool
}
DeriveKey允许从已有秘钥派生一组新的秘钥(比如通过HMAC或者重新随机生成)。通过适当的opts可以选择不同的派生方法。
同GenKey,对于开发者来说,至少需要为指定生成秘钥的算法和是否是短期秘钥。如果是长期秘钥的话,则需要通过SKI来完成存储和索引。
同GenKey,值得注意的是,除了这两个方法,其他任何的参数,你都可以在实现此接口DeriveKeyOpts的时候加上。
2.1.6 签名验签能力
bccsp.go
// Sign signs digest using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
//
// Note that when a signature of a hash of a larger message is needed,
// the caller is responsible for hashing the larger message and passing
// the hash (as digest).
Sign(k Key, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (signature []byte, err error)
// Verify verifies signature against key k and digest
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Verify(k Key, signature, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (valid bool, err error)
bccsp.go
// SignerOpts contains options for signing with a CSP.
type SignerOpts interface{}
BCCSP通过Sign,Verify提供签名验签。
通过秘钥的种类来决定签名验签的算法,比如传入ECDSA的秘钥就使用ECDSA的签名算法。
其他任何的参数,你都可以在实现此接口SignerOpts的时候加上。
2.1.7 加解密能力
bccsp.go
// Encrypt encrypts plaintext using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Encrypt(k Key, plaintext []byte, opts EncrypterOpts) (ciphertext []byte, err error)
// Decrypt decrypts ciphertext using key k.
// The opts argument should be appropriate for the algorithm used.
Decrypt(k Key, ciphertext []byte, opts DecrypterOpts) (plaintext []byte, err error)
bccsp.go
// EncrypterOpts contains options for encrypting with a CSP.
type EncrypterOpts interface{}
// DecrypterOpts contains options for decrypting with a CSP.
type DecrypterOpts interface{}
BCCSP通过Encrypt,Decrypt提供加密/解密。
通过不同种类的秘钥类型和opts来决定使用的加密算法(译注:这和签名验签不同,这里会使用opts来决定使用的模式)。 举个栗子,如果秘钥是AES的,那么opts就会用来决定操作的模式。
可以在实现EncrypterOpts/ DecrypterOpts的时候添加任何你想要定制的参数。(译注: 这里原文注释有错误,写成了SignerOpts)
2.1.8 摘要能力 译者增加表述
(原文由于版本原因,没有列出hash)
bccsp.go
// Hash hashes messages msg using options opts.
// If opts is nil, the default hash function will be used.
Hash(msg []byte, opts HashOpts) (hash []byte, err error)
// GetHash returns and instance of hash.Hash using options opts.
// If opts is nil, the default hash function will be returned.
GetHash(opts HashOpts) (h hash.Hash, err error)
bccsp.go
// HashOpts contains options for hashing with a CSP.
type HashOpts interface {
// Algorithm returns the hash algorithm identifier (to be used).
Algorithm() string
}
BCCSP通过Hash来提供摘要能力
不同种类的hash算法可以通过不同的opts来获取(比如md5或者SHA256)
2.2 国密支持的解决思路
首先了解一下进行国密支持需要关注哪几个方面内容。分为4个层次:BCCSP,算法实现,X509证书支持和秘钥相关内容。
- 第一点BCCSP前面已经介绍了,可以通过改造sw(software)和pkcs11部分工作,提供软件和硬件层面的支持。sw提供一套密码算法集,可以考虑在中间加入国密算法接口支持。
- 第二点是国密算法具体的实现,SM2,SM3,SM4现在是公开标准,可以在公开渠道获取到算法细则,现在也有不同语言版本的实现可以参考。
- 第三点是X509证书支持,Fabric中证书创建和解析相关是加入Golang中的X509证书模块完成的,但是现在x509模块只支持RSA和ECDSA两种算法模式,所以如果直接引入原版的X509证书解析的话,在证书国密支持方面会比较棘手,这个问题在后面会进一步讨论。另外X509里面会根据OID来指定所使用的签名算法,签名参数等信息,这部分可以参考“GMT 0015-2012”规范附件部分定义。
- 第四点是秘钥相关部分,其中包括通过证书封装的公匙部分,还有本地存储的私钥部分。特别注意到sw中算法是可以通过秘钥的类型来动态选择的,并且能够更灵活应用,带格式的秘密存储是有必要的。比如现在通过pkcs1来存储RSA密钥,通过pkcs8来存储ECDSA密钥,SM2和ECDSA结构类似,也可以参考使用PKCS8来进行格式存储。
| PKCS标准汇总 | 版本 | 名称 | 简介 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PKCS #1 | 2.1 | RSA密码编译标准(RSA Cryptography Standard) | 定义了RSA的数理基础、公/私钥格式,以及加/解密、签/验章的流程。1.5版本曾经遭到攻击。 |
| PKCS #2 | - | 撤销 | 原本是用以规范RSA加密摘要的转换方式,现已被纳入PKCS#1之中。 |
| PKCS #3 | 1.4 | DH密钥协议标准(Diffie-Hellman key agreement Standard) | 规范以DH密钥协议为基础的密钥协议标准。其功能,可以让两方通过金议协议,拟定一把会议密钥(Session key)。 |
| PKCS #4 | - | 撤销 | 原本用以规范转换RSA密钥的流程。已被纳入PKCS#1之中。 |
| PKCS #5 | 2.0 | 密码基植加密标准(Password-based Encryption Standard) | 参见RFC 2898与PBKDF2。 |
| PKCS #6 | 1.5 | 证书扩展语法标准(Extended-Certificate Syntax Standard) | 将原本X.509的证书格式标准加以扩充。 |
| PKCS #7 | 1.5 | 密码消息语法标准(Cryptographic Message Syntax Standard) | 参见RFC 2315。规范了以公开密钥基础设施(PKI)所产生之签名/密文之格式。其目的一样是为了拓展数字证书的应用。其中,包含了S/MIME与CMS。 |
| PKCS #8 | 1.2 | 私钥消息表示标准(Private-Key Information Syntax Standard). | Apache读取证书私钥的标准。 |
| PKCS #9 | 2.0 | 选择属性格式(Selected Attribute Types) | 定义PKCS#6、7、8、10的选择属性格式。 |
| PKCS #10 | 1.7 | 证书申请标准(Certification Request Standard) | 参见RFC 2986。规范了向证书中心申请证书之CSR(certificate signing request)的格式。 |
| PKCS #11 | 2.20 | 密码设备标准接口(Cryptographic Token Interface (Cryptoki)) | 定义了密码设备的应用程序接口(API)之规格。 |
| PKCS #12 | 1.0 | 个人消息交换标准(Personal Information Exchange Syntax Standard) | 定义了包含私钥与公钥证书(public key certificate)的文件格式。私钥采密码(password)保护。常见的PFX就履行了PKCS#12。 |
| PKCS #13 | – | 椭圆曲线密码学标准(Elliptic curve cryptography Standard) | 制定中。规范以椭圆曲线密码学为基础所发展之密码技术应用。椭圆曲线密码学是新的密码学技术,其强度与效率皆比现行以指数运算为基础之密码学算法来的优秀。然而,该算法的应用尚不普及。 |
| PKCS #14 | – | 拟随机数产生器标准(Pseudo-random Number Generation) | 制定中。规范拟随机数产生器的使用与设计。 |
| PKCS #15 | 1.1 | 密码设备消息格式标准(Cryptographic Token Information Format Standard) | 定义了密码设备内部数据的组织结构。 |
前面介绍了国密支持所需要关注的问题。除了BCCSP层面外,算法实现和X509证书支持Fabric是是直接引用的golang下面的标准库来支持的。
而标准库并没有对国密算法进行支持,所以这里引出了两种思路。
- 一种是把算法实现和X509的证书支持都放在Fabric层面来做。这种方式的好处是不用动golang的标准库,所有工作都收敛到Fabric上。但是缺点是X509的证书部分需要在上层做定制,所有引入证书的地方,都需要做调整。代码也会有较多冗余部分。
- 另一种是将算法实现和X509国密支持部分放在golang的标准lib上,这样面料层面的适配就会少很多。这种缺点的是golang部分需要做定制,特别是牵扯到用户环境还要同时考虑到本地和docker环境两种方式下,golang层面应该如何完成适配。后面会着重说这种方式的解决思路
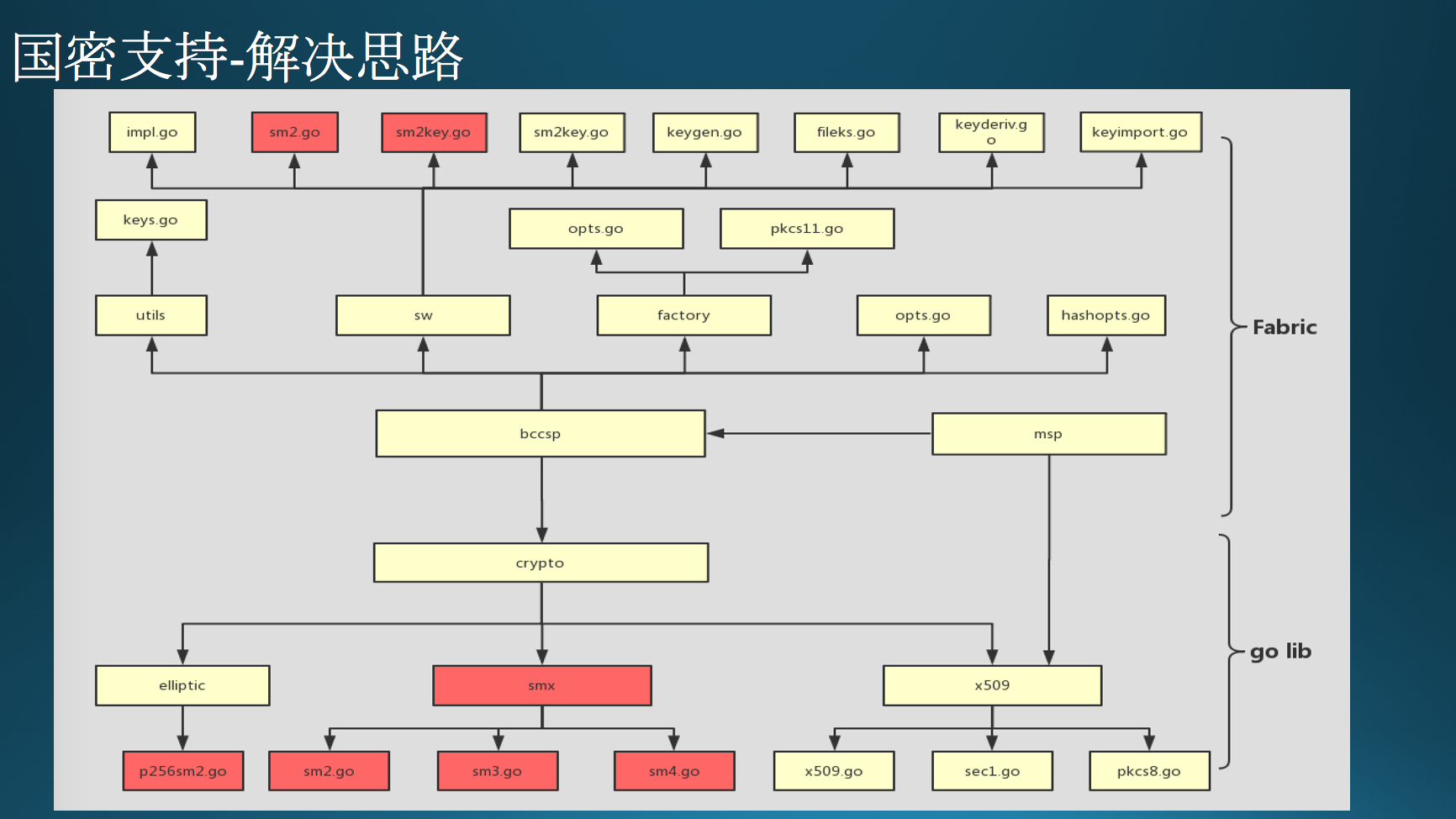
第二种支持方式个人认为较前者更优,能够在不影响整个Fabric架构的前提下,更好的完成国密支持,并且可以进行动态配置需要使用的算法,不失灵活性。
图中所示为整个国密支持中,Fabric和golang lib层面所需要定制的部分。黄色代表需要修改部分,红色代表新增部分。
上层为Fabric需要处理的模块,主要集中在BCCSP部分。下层为golang层面需要处理的模块,主要集中在crypto中。

如果想在golang层面做支持的话,那么整个系统的构建环境就需要做一定的定制。
对于本地的构建环境来说,需要将golang替换成国密版本支持的。
其中,go源码的修改,需要添加sm包,还需要修改和x509相关的文件。
对于docker相关的,需要更改docker image中golang层的支持.Fabric中,对golang的支持,是放在fabric-baseimage中的.baseimage中,将特定版本的环境打包到镜像中,提供底层的支持。
关于baseimage的修改:我们首先从官方仓库去克隆代码。我们先看下Dockerfile。
FROM adoptopenjdk:8u222-b10-jdk-openj9-0.15.1
COPY scripts /tmp/scripts
RUN cd /tmp/scripts && \
common/packages.sh && \
common/setup.sh && \
docker/fixup.sh && \
common/cleanup.sh && \
rm -rf /tmp/scripts
ENV GOPATH=/opt/gopath
ENV GOROOT=/opt/go
#ENV GOCACHE=off
ENV PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin:$GOPATH/bin
可以看到依赖adoptopenjdk,此外,如果我们使用的go的版本是1.12及以上的话,需要把ENV GOCACHE=off注释掉。
值得注意的是,我们在packages.sh需要下载一些软件,但是众所周知的原因,导致极大可能下载失败,所以我们要把源替换掉,我们准备好国内的sources.list放在scripts目录下:
然后在scripts/common/packages.sh中替换sources.list,即 cp sources.list /etc/apt/
接下来是核心部分,我们需要加入go的国密的支持,首先我们把国密版本的go放在scripts目录下,然后我们需要修改scripts/common/setup.sh中go的安装部分,我们直接把go复制到$GOROOT即可,即
cp -r scripts/go $GOROOT
最后我们生成baseimage镜像即可:docker build -f config/baseimage/Dockerfile -t hyperledger/fabric-baseimage-sm:0.4.14 .
然后执行docker run -it imageid /bin/bash,看看go是不是国密版本的。

下面说一下pkcs11的国密支持,这块的解决思路和sw的相同,sw的关注点pkcs11也同样需要关注。这里还需要注意的是pkcs11本身是不支持国密算法的。也就是对说如果要做到支持需要对PKCS11的接口标准也做一定的更改,所以对设备厂商来说,每家可能对接口标准的定制都不太一样,所以由于不标准,导致平台适配会出现问题。
国家密码管理局在2011年也制定了相关的接口标准,接口标准叫做SKF。所以另一种考虑思路是,做国密支持可以通过SKF标准来做。
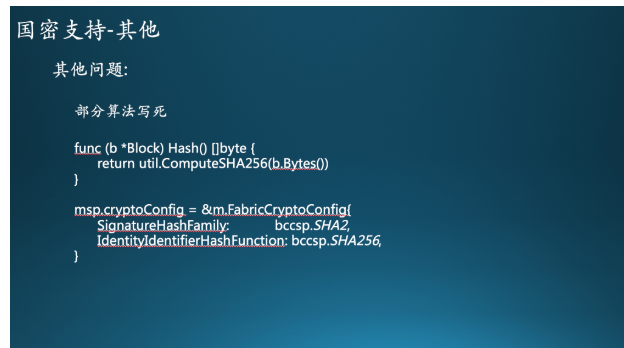
那么国密支持还有一些问题,是需要注意的,系统中有些调用算法的部分,是硬代码进去的,比如区块的哈希部分,区块的哈希部分现在是写死成sha256的,但是值得注意的是,通道配置部分里面是有配置区块哈希算法的。可以通过配置HashingAlgorithm参数来指定使用的哈希算法,可惜当前版本并没有开放配置功能。
当然另一个问题是,是否系统中所有的算法都需要替换成国密标准,这个也是需要考虑的地方。
除此之外,作为整个系统来看,Fabric做国密支持,也少不了外围的支持,包括CA和client-sdk
- CA可以考虑使用现有的国密CA系统,也可以考虑通过Fabric-CA来做搭建,fabric-ca沿用fabric中的BCCSP套件,所以支持上难度也不大。
- client-sdk现在有很多种版本,所以有一些工作量在里面。好在每个版本的密码服务套件都是插件化的,比如节点里面可以实现一套支持国密的CryptoSuite来提供支持,当然节点里面还是要对jsrsasign模块X509相关部分进行定制。
数据的流转。
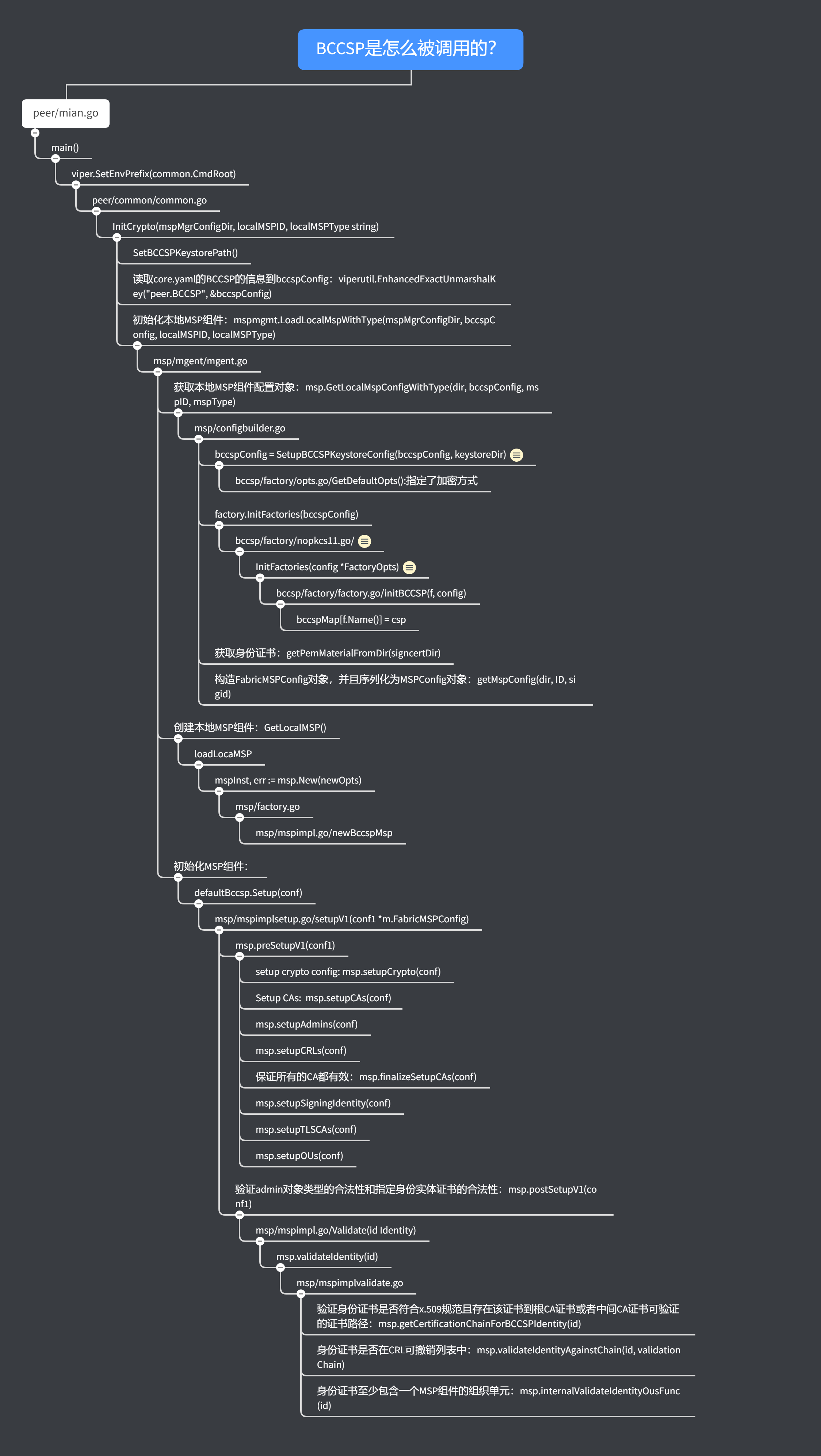
3. Fabric的修改细节
我们可以看到,总共有下面的文件受到了影响。
bccsp/factory/gmfactory.go | 42 +
bccsp/factory/nopkcs11.go | 4 +-
bccsp/factory/pkcs11.go | 4 +-
bccsp/gm/fileks.go | 407 ++
bccsp/gm/impl.go | 391 ++
bccsp/gm/keys.go | 415 ++
bccsp/gm/sm2.go | 78 +
bccsp/gm/sm2key.go | 119 +
bccsp/gm/sm3sig.go | 51 +
bccsp/sm2opts.go | 131 +
bccsp/utils/keys.go | 3 +-
common/tools/cryptogen/ca/generator.go | 2 +
common/tools/cryptogen/ca/generatorsm.go | 241 +
common/tools/cryptogen/csp/csp.go | 2 +
common/tools/cryptogen/csp/cspsm.go | 164 +
common/tools/cryptogen/main.go | 2 +
common/tools/cryptogen/mainsm.go | 719 +++
common/tools/cryptogen/msp/generator.go | 2 +
common/tools/cryptogen/msp/generatorsm.go | 284 +
core/common/validation/msgvalidation.go | 2 +-
docker-env.mk | 2 +-
examples/plugins/smPlugin/fileks.go | 407 ++
examples/plugins/smPlugin/impl.go | 372 ++
examples/plugins/smPlugin/keys.go | 415 ++
examples/plugins/smPlugin/sm2.go | 78 +
examples/plugins/smPlugin/sm2key.go | 119 +
msp/cert.go | 3 +-
msp/identities.go | 32 +-
msp/mspimpl.go | 3 +-
msp/mspimplsetup.go | 3 +-
msp/mspimplvalidate.go | 3 +-
.../crypto/internal/randutil/randutil.go | 38 +
.../crypto/internal/subtle/aliasing.go | 34 +
.../internal/subtle/aliasing_appengine.go | 37 +
.../crypto/internal/subtle/aliasing_test.go | 50 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm2/p256sm2.go | 54 +
.../github.com/flyinox/crypto/sm/sm2/sm2.go | 224 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm2/sm2_test.go | 223 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm2/sm2enc.go | 168 +
.../github.com/flyinox/crypto/sm/sm3/sm3.go | 149 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm3/sm3_test.go | 83 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm3/sm3hash.go | 172 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm4/cipher.go | 42 +
.../flyinox/crypto/sm/sm4/cipher_test.go | 65 +
.../github.com/flyinox/crypto/sm/sm4/sm4.go | 125 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/cert_pool.go | 170 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/example_test.go | 134 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/pem_decrypt.go | 240 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/pem_decrypt_test.go | 247 +
.../github.com/flyinox/crypto/x509/pkcs1.go | 121 +
.../github.com/flyinox/crypto/x509/pkcs8.go | 55 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/pkcs8_test.go | 28 +
vendor/github.com/flyinox/crypto/x509/root.go | 22 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_bsd.go | 15 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_cgo_darwin.go | 236 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_darwin.go | 264 +
.../crypto/x509/root_darwin_arm_gen.go | 192 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_darwin_armx.go | 4908 +++++++++++++++++
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_darwin_test.go | 80 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_linux.go | 14 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_nacl.go | 8 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_nocgo_darwin.go | 11 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_plan9.go | 37 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_solaris.go | 12 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_unix.go | 88 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_unix_test.go | 127 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/root_windows.go | 266 +
vendor/github.com/flyinox/crypto/x509/sec1.go | 162 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/sec1_test.go | 44 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/sha2_windows_test.go | 19 +
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/test-file.crt | 32 +
.../github.com/flyinox/crypto/x509/verify.go | 565 ++
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/verify_test.go | 1694 ++++++
vendor/github.com/flyinox/crypto/x509/x509.go | 2421 ++++++++
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/x509_test.go | 1425 +++++
.../flyinox/crypto/x509/x509_test_import.go | 53 +
76 files changed, 19640 insertions(+), 14 deletions(-)
3.1 vendor/github.com/flyinox/crypto
正如前文所说,我们将在golang的标准库层来支持国密算法,我们把实现的国密算法以及x509规范都放入vendor目录下,即vendor/github.com/flyinox。
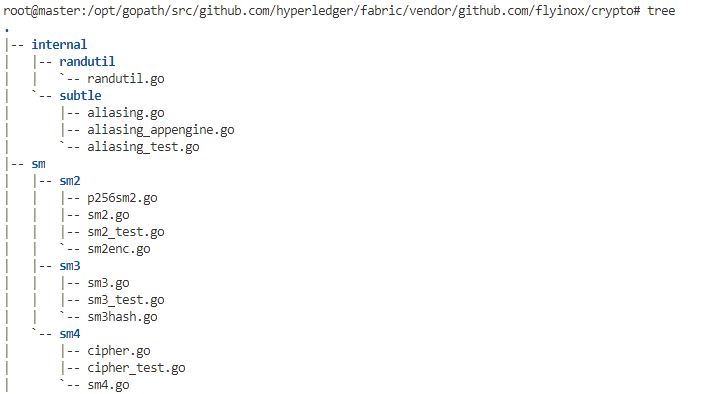
- internal
- randutil
- randutil.go:生成随机数
- subtle
- aliasing.go
- aliasing_appengine.go
- aliasing_test.go
- randutil
- sm(加密算法)
- sm2
- sm2.go:非对称加密
- sm2_test.go:
- sm2enc.go:
- p256sm2.go:修改椭圆曲线为sm2推荐的。
- sm3
- sm3.go:hash算法
- sm3_test.go
- sm3hash.go
- sm4
- sm4.go;对称加密
- cipher.go
- cipher_test.go
- sm2
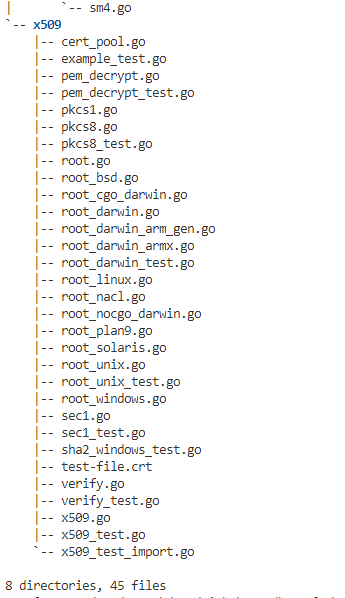
- x509(证书支持) |– cert_pool.go:证书池 |– example_test.go |– pem_decrypt.go:证书加密 |– pem_decrypt_test.go |– pkcs1.go:定义RSA公开密钥算法加密和签名机制 |– pkcs8.go:描述私有密钥信息格式,该信息包括公开密钥算法的私有密钥以及可选的属性集等。 |– pkcs8_test.go |– root.go |– root_bsd.go |– root_cgo_darwin.go |– root_darwin.go |– root_darwin_arm_gen.go |– root_darwin_armx.go |– root_darwin_test.go |– root_linux.go |– root_nacl.go |– root_nocgo_darwin.go |– root_plan9.go |– root_solaris.go |– root_unix.go |– root_unix_test.go |– root_windows.go |– sec1.go |– sec1_test.go |– sha2_windows_test.go |– test-file.crt |– verify.go |– verify_test.go |– x509.go |– x509_test.go `– x509_test_import.go
3.2 bccsp
3.2.1 gm
提供了国密算法的相关实现。
在gm文件夹中新增了:sm2.go,sm2key.go,sm3sig.go,fileks.go,impl.go,keys.go六个文件。
| 功能 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|
| sm2.go | 封装了标准库,提供非对称加密功能 | |
| sm2key.go | sm2密钥相关 | |
| sm3sig.go | hash算法相关 | |
| fileks.go | KeyStore文件的初始化,存储,加载,创建和搜索 | |
| impl.go | 封装了gm的算法 | |
| keys.go | 封装了密钥相关 |
3.2.2 sm2opts.go
3.2.3 factory
| 功能 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|
| gmfactory.go | 提供了获取工厂名字的方法,使用Opts返回BCCSP的实例。 | |
| nopkcs11.go | 工厂的初始化和从opt获取BCCSP,SW替换为GM | 和下面的区别在于,nopkcs11表示使用软件加密。默认为nopkcs11。 |
| pkcs11.go | 工厂的初始化和从opt获取BCCSP,SW替换为GM | pkcs11表示使用硬件加密 |
3.2.4 utils/keys.go
把我们自己实现的国密版本的crypto/x509替换掉原来的
3.3 common/tools/cryptogen
下面这些是用于生成国密版本的cryptogen工具。
| 功能 | |
|---|---|
| csp/csp.go | |
| csp/cspsm.go | 创建私钥,存储在keystorePath,支持ECDSA和SM2。从keystorePath加载私钥。获取公钥 |
| ca/generator.go | |
| ca/generatorsm.go | 创建CA实例,对证书签名, |
| msp/generator.go | |
| msp/generatorsm.go | 生成msp文件夹,区别在于是否keystore和signcerts文件 |
| main.go | // +build IGNORE 表示编译的时候忽略该文件 |
| mainsm.go | 生成具体的配置文件 |
3.4 msp
| 功能 | 修改 | |
|---|---|---|
| cert.go | x509替换为国密 | |
| identities.go | x509替换为国密 | |
| mspimpl.go | 增加了国密部分 | |
| mspimplsetup.go | ||
| mspimplvalidate.go |
3.5 core/common/validation
msgvalidation.go
3.6 docker-env.mk
DOCKER_DYNAMIC_LINK原来的false改为了true
3.7 examples/plugins/smPlugin
| 功能 | |
|---|---|
| fileks.go | |
| impl.go | |
| keys.go | |
| sm2.go | |
| sm2key.go |
3.8 验证
运行下example,我们看到了熟悉的END-E2E。
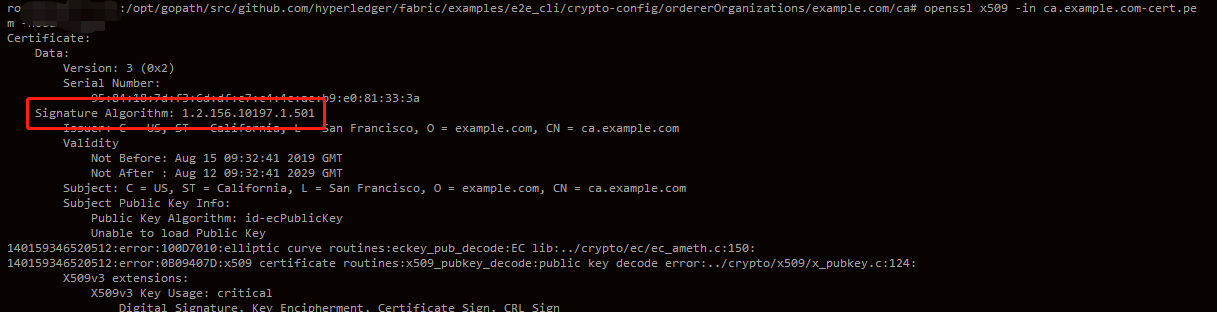
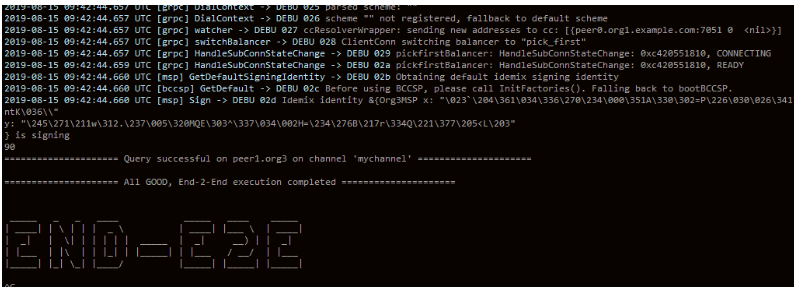 再来检查下,是不是使用的国密算法,我们使用openssl工具来检查下证书使用的算法,我们可以看到使用的签名算法是1.2.156.10197.1.501,这个就是国密使用的算法。
再来检查下,是不是使用的国密算法,我们使用openssl工具来检查下证书使用的算法,我们可以看到使用的签名算法是1.2.156.10197.1.501,这个就是国密使用的算法。
openssl x509 -in ca.example.com-cert.pem -noout -text