前言
我们知道,对于一个程序来讲,其核心是数据结构和算法。正如我们之前学习TCP/IP协议的时候。对于Fabric来讲,我们很关心区块是怎么存储的,那么了解其数据结构是很重要的,本文将带你了解Fabric区块的数据结构。
我们先来看2张图,第一张图是区块的结构,第二张图是数据结构的定义图,两张图配合着看,我会对字段进行解释。给出这2个图的意义在于我们分析的时候,不会迷失方向。
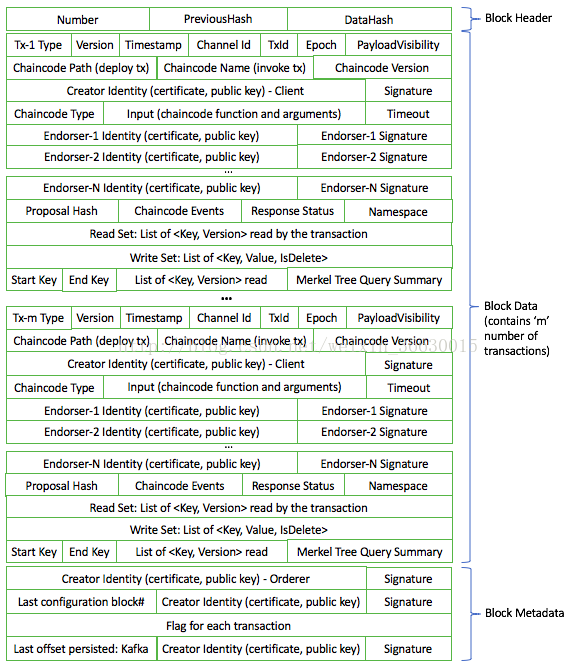
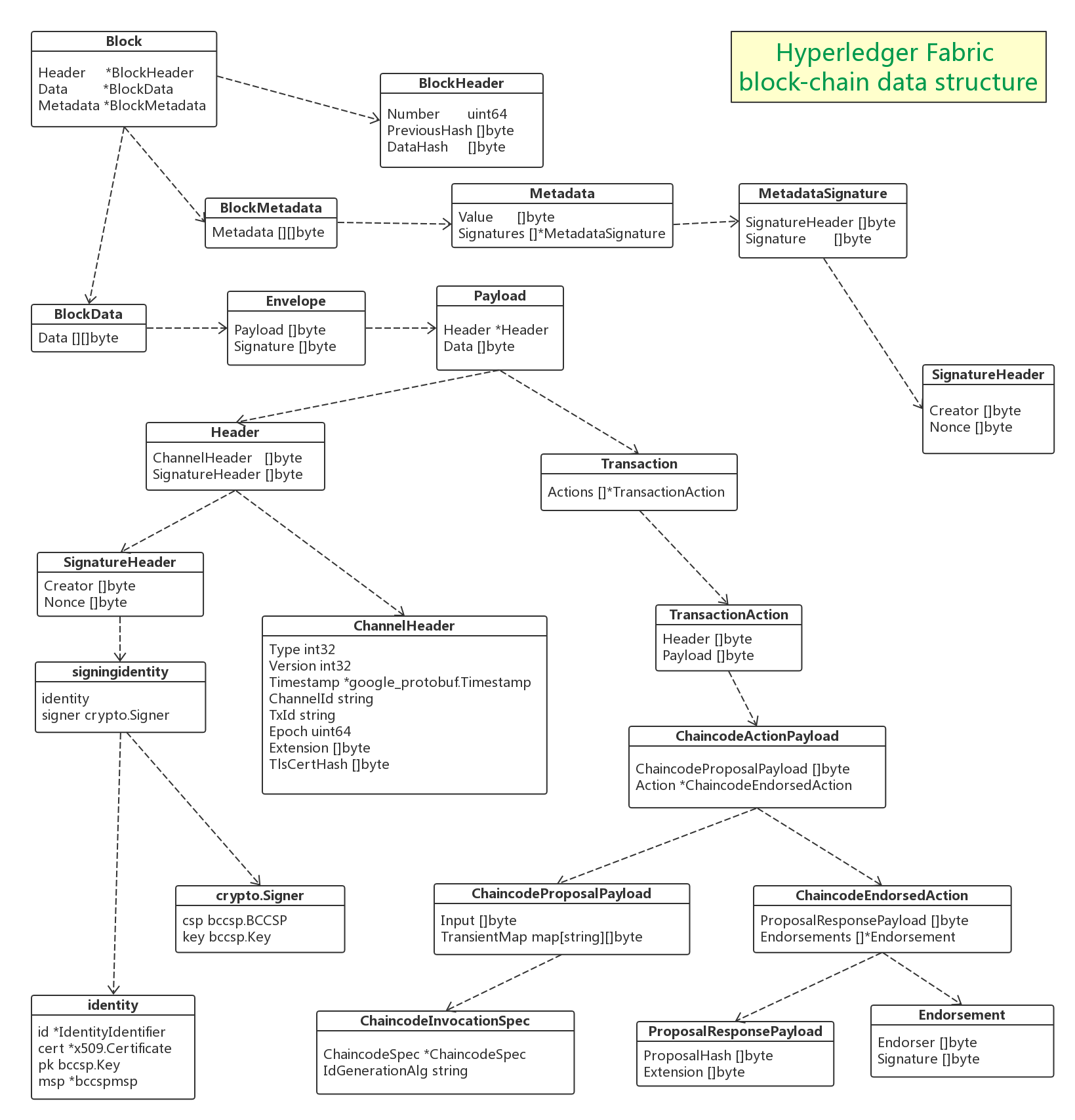
Block
Block是区块链数据结构里面的一个最基本的元素。
// This is finalized block structure to be shared among the orderer and peer
// Note that the BlockHeader chains to the previous BlockHeader, and the BlockData hash is embedded
// in the BlockHeader. This makes it natural and obvious that the Data is included in the hash, but
// the Metadata is not.
type Block struct {
Header *BlockHeader `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=header" json:"header,omitempty"`
Data *BlockData `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=data" json:"data,omitempty"`
Metadata *BlockMetadata `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=metadata" json:"metadata,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
从这个结构体的定义可以看出,一个Block里面包含了三种类型的数据,
- Header,即区块头,这里又包含了三项数据,包括:
- Number:Block Number,即区块号,用来标识每个区块。
- PreviousHash:前一个区块头的hash值
- DataHash:Data域的hash值,这里没有包含Metadata
- Data,即区块数据,这里包含的就是所有的Transaction数据
- Metadata,元数据,这里记录的是一些辅助信息,包括:
- Metadata[BlockMetadataIndex_SIGNATURES]:签名信息
- Metadata[BlockMetadataIndex_LAST_CONFIG]:Channel的最新配置区块索引
- Metadata[BlockMetadataIndex_TRANSACTIONS_FILTER]:交易是否合法的标记
- Metadata[BlockMetadataIndex_ORDERER]:Channel的排序服务信息
这里是BlockHeader结构体的定义,这里面的三项数据前面已经有说明了:
// This is finalized block structure to be shared among the orderer and peer
// Note that the BlockHeader chains to the previous BlockHeader, and the BlockData hash is embedded
// in the BlockHeader. This makes it natural and obvious that the Data is included in the hash, but
// the Metadata is not.
type Block struct {
Header *BlockHeader `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=header" json:"header,omitempty"`
Data *BlockData `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=data" json:"data,omitempty"`
Metadata *BlockMetadata `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=metadata" json:"metadata,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
这里是BlockMetadata的定义:
type BlockMetadata struct {
Metadata [][]byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=metadata,proto3" json:"metadata,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
我们可以看到,BlockMetadata结构体中的Metadata域是一个byte类型的二维数组,而这个数据是由下面的Metadata结构体序列化而来的。
// Metadata is a common structure to be used to encode block metadata
type Metadata struct {
Value []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=value,proto3" json:"value,omitempty"`
Signatures []*MetadataSignature `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=signatures" json:"signatures,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
从这个定义中可以知道,元数据就是由一个value和相应的签名组成。
总结下:Block包含BlockHeader,BlockData和BlockMetadata。
##BlockHeader
这里不再详细分析,上面已经有了。
BlockData
下面我们来看下核心的BlockData。
这个结构体只有一个数据Data,又是一个byte类型的二维数组。和前面的Metadata一样,这个也是由另外一个数据结构序列化而来的。
type BlockData struct {
Data [][]byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=data,proto3" json:"data,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
// Envelope wraps a Payload with a signature so that the message may be authenticated
type Envelope struct {
// A marshaled Payload
Payload []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=payload,proto3" json:"payload,omitempty"`
// A signature by the creator specified in the Payload header
Signature []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=signature,proto3" json:"signature,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
在Envelope这个结构体中,Signature就是对Payload数据的签名,这个数据在网络中传输的时候,这个签名用于对数据做有效性验证。Payload本身又是由另外一个数据结构序列化而来的。
Payload
// Payload is the message contents (and header to allow for signing)
type Payload struct {
// Header is included to provide identity and prevent replay
Header *Header `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=header" json:"header,omitempty"`
// Data, the encoding of which is defined by the type in the header
Data []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=data,proto3" json:"data,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
Payload,中文直译是负载的意思,也就是说具体承载交易数据。
header
这里包含一个header,这个header带有类型,负责描述这个payload的性质以及如何解析data字段。 另外header中还包含有创建者的信息和一个随机数,以及用来标识逻辑时间窗口的时期信息,这个时间窗口数据用于抵御重放攻击。
ChannelHeader
同样,Header中的ChannelHeader字段是由一个ChannelHeader的结构序列化而来的。
type Header struct {
ChannelHeader []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=channel_header,json=channelHeader,proto3" json:"channel_header,omitempty"`
SignatureHeader []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=signature_header,json=signatureHeader,proto3" json:"signature_header,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
// Header is a generic replay prevention and identity message to include in a signed payload
type ChannelHeader struct {
Type int32 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=type" json:"type,omitempty"`
// Version indicates message protocol version
Version int32 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=version" json:"version,omitempty"`
// Timestamp is the local time when the message was created
// by the sender
Timestamp *timestamp.Timestamp `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=timestamp" json:"timestamp,omitempty"`
// Identifier of the channel this message is bound for
ChannelId string `protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=channel_id,json=channelId" json:"channel_id,omitempty"`
// An unique identifier that is used end-to-end.
// - set by higher layers such as end user or SDK
// - passed to the endorser (which will check for uniqueness)
// - as the header is passed along unchanged, it will be
// be retrieved by the committer (uniqueness check here as well)
// - to be stored in the ledger
TxId string `protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=tx_id,json=txId" json:"tx_id,omitempty"`
// The epoch in which this header was generated, where epoch is defined based on block height
// Epoch in which the response has been generated. This field identifies a
// logical window of time. A proposal response is accepted by a peer only if
// two conditions hold:
// 1. the epoch specified in the message is the current epoch
// 2. this message has been only seen once during this epoch (i.e. it hasn't
// been replayed)
Epoch uint64 `protobuf:"varint,6,opt,name=epoch" json:"epoch,omitempty"`
// Extension that may be attached based on the header type
Extension []byte `protobuf:"bytes,7,opt,name=extension,proto3" json:"extension,omitempty"`
// If mutual TLS is employed, this represents
// the hash of the client's TLS certificate
TlsCertHash []byte `protobuf:"bytes,8,opt,name=tls_cert_hash,json=tlsCertHash,proto3" json:"tls_cert_hash,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
- Type:ChannelHeader中的Type,定义了这个Payload包含的是那种类型的消息,其中,1~10000的数值定义由系统保留。目前有如下的类型定义:
- MESSAGE = 0; // 不透明的消息类型
- CONFIG = 1; // Channel配置消息
- CONFIG_UPDATE = 2; // Channel配置更新的交易
- ENDORSER_TRANSACTION = 3; // 客户端通过SDK向Endorser节点提交交易提案
- ORDERER_TRANSACTION = 4; // 排序节点内部使用
- DELIVER_SEEK_INFO = 5; // 用于指示Deliver API查找信息
- CHAINCODE_PACKAGE = 6; // 用户安装链码的时候打包链码组件
- PEER_RESOURCE_UPDATE = 7; // 用于peer资源更新的时候,对更新信息做编码
- Version:指定消息协议的版本号
- Timestamp:定义发件人发出消息时候的本地时间,这里使用了Google Protobuf框架里面定义的时间格式
- ChannelId:指定了这个消息是绑定在哪一个Channel上的。我们知道Fabric中定义了Multi Channel的概念,绑定到特定的Channel上面,意味着这个消息只能由这个特定的Channel处理,其他的Channel是不能查看这个消息的
- TxId:一个唯一的ID,通常由更高层设定,比如用户或者SDK。这个数据传递给背书节点的时候,背书节点会检查其唯一性。当消息被正确传递的时候,记账节点也会去检索这条消息,同时也会去检查其唯一性。最终,这个数据会被保存在账本中
- Epoch:这个数据基于区块的高度(区块号)来定义,指定了这条消息的时间窗口,只有在满足以下两个条件的情况下,目的节点才会接受这条消息:
- 消息中指定的时间信息是当前时期
- 在这一个时间段内,这条消息只出现了一次(预防重放攻击)
- Extension:根据header type,不同的特定消息会附加自己特定的扩展数据
- TlsCertHash:如果使用了共同TLS,则这个数据指示了客户端的TLS证书
SignatureHeader
type SignatureHeader struct {
// Creator of the message, a marshaled msp.SerializedIdentity
Creator []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=creator,proto3" json:"creator,omitempty"`
// Arbitrary number that may only be used once. Can be used to detect replay attacks.
Nonce []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=nonce,proto3" json:"nonce,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
SignatureHeader由signingidentity序列化而成:
type signingidentity struct {
// we embed everything from a base identity
identity
// signer corresponds to the object that can produce signatures from this identity
signer crypto.Signer
}
type identity struct {
// id contains the identifier (MSPID and identity identifier) for this instance
id *IdentityIdentifier
// cert contains the x.509 certificate that signs the public key of this instance
cert *x509.Certificate
// this is the public key of this instance
pk bccsp.Key
// reference to the MSP that "owns" this identity
msp *bccspmsp
}
// Signer is an interface for an opaque private key that can be used for
// signing operations. For example, an RSA key kept in a hardware module.
type Signer interface {
// Public returns the public key corresponding to the opaque,
// private key.
Public() PublicKey
// Sign signs digest with the private key, possibly using entropy from
// rand. For an RSA key, the resulting signature should be either a
// PKCS#1 v1.5 or PSS signature (as indicated by opts). For an (EC)DSA
// key, it should be a DER-serialised, ASN.1 signature structure.
//
// Hash implements the SignerOpts interface and, in most cases, one can
// simply pass in the hash function used as opts. Sign may also attempt
// to type assert opts to other types in order to obtain algorithm
// specific values. See the documentation in each package for details.
//
// Note that when a signature of a hash of a larger message is needed,
// the caller is responsible for hashing the larger message and passing
// the hash (as digest) and the hash function (as opts) to Sign.
Sign(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts SignerOpts) (signature []byte, err error)
}
Transaction
在Payload结构体中的Data,是由Transaction结构体序列化而来的,
// The transaction to be sent to the ordering service. A transaction contains
// one or more TransactionAction. Each TransactionAction binds a proposal to
// potentially multiple actions. The transaction is atomic meaning that either
// all actions in the transaction will be committed or none will. Note that
// while a Transaction might include more than one Header, the Header.creator
// field must be the same in each.
// A single client is free to issue a number of independent Proposal, each with
// their header (Header) and request payload (ChaincodeProposalPayload). Each
// proposal is independently endorsed generating an action
// (ProposalResponsePayload) with one signature per Endorser. Any number of
// independent proposals (and their action) might be included in a transaction
// to ensure that they are treated atomically.
type Transaction struct {
// The payload is an array of TransactionAction. An array is necessary to
// accommodate multiple actions per transaction
Actions []*TransactionAction `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=actions" json:"actions,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
客户端发送到排序服务节点的数据就是由这个Transaction结构体定义的,一个Transaction结构又包含了一个或者多个TransactionAction数据(因为需要多个背书节点)。每一个TransactionAction数据就是一个交易提案,可能包含有多个Action。Transaction结构数据是原子性的,这就意味着,一条Transaction结构数据中包含的所有Action要么是全部被写入账本,要么是全部丢弃。这里需要注意的是:一条Transaction结构数据中可能会包含有多个Header,但是所有这些Header的Creator都必须是相同的,这也就意味着所有这些Action都是由同一个用户发起的。
一个单独的客户端可以提交一系列相互独立的提案,每一个提案都可以包含它自己的header和Payload(ChaincodeProposalPayload)。背书节点会对每一个提案单独做背书并且产生独立的Action
每一个独立的背书节点都会给Payload(ChaincodeProposalPayload)打上自己的签名,任意数量的提案以及这些提案包含的Action都可以打包到一条Transaction数据之中,当然这样的一条Transaction数据会被当做一条原子数据来处理。
Transaction结构体本身是由TransactionAction的数组组成。
TransactionAction
// TransactionAction binds a proposal to its action. The type field in the
// header dictates the type of action to be applied to the ledger.
type TransactionAction struct {
// The header of the proposal action, which is the proposal header
Header []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=header,proto3" json:"header,omitempty"`
// The payload of the action as defined by the type in the header For
// chaincode, it's the bytes of ChaincodeActionPayload
Payload []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=payload,proto3" json:"payload,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
这个结构体为每一个Action绑定了一个提案,在Header字段中的type指定了这个action的分类。
这个结构体中的Payload具体类型则是由Header中的type定义的,它是ChaincodeActionPayload结构体的序列化数据。
// ChaincodeActionPayload is the message to be used for the TransactionAction's
// payload when the Header's type is set to CHAINCODE. It carries the
// chaincodeProposalPayload and an endorsed action to apply to the ledger.
type ChaincodeActionPayload struct {
// This field contains the bytes of the ChaincodeProposalPayload message from
// the original invocation (essentially the arguments) after the application
// of the visibility function. The main visibility modes are "full" (the
// entire ChaincodeProposalPayload message is included here), "hash" (only
// the hash of the ChaincodeProposalPayload message is included) or
// "nothing". This field will be used to check the consistency of
// ProposalResponsePayload.proposalHash. For the CHAINCODE type,
// ProposalResponsePayload.proposalHash is supposed to be H(ProposalHeader ||
// f(ChaincodeProposalPayload)) where f is the visibility function.
ChaincodeProposalPayload []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=chaincode_proposal_payload,json=chaincodeProposalPayload,proto3" json:"chaincode_proposal_payload,omitempty"`
// The list of actions to apply to the ledger
Action *ChaincodeEndorsedAction `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=action" json:"action,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
ChaincodeProposalPayload
// ChaincodeProposalPayload is the Proposal's payload message to be used when
// the Header's type is CHAINCODE. It contains the arguments for this
// invocation.
type ChaincodeProposalPayload struct {
// Input contains the arguments for this invocation. If this invocation
// deploys a new chaincode, ESCC/VSCC are part of this field.
// This is usually a marshaled ChaincodeInvocationSpec
Input []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=input,proto3" json:"input,omitempty"`
// TransientMap contains data (e.g. cryptographic material) that might be used
// to implement some form of application-level confidentiality. The contents
// of this field are supposed to always be omitted from the transaction and
// excluded from the ledger.
TransientMap map[string][]byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=TransientMap" json:"TransientMap,omitempty" protobuf_key:"bytes,1,opt,name=key" protobuf_val:"bytes,2,opt,name=value,proto3"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
// Carries the chaincode function and its arguments.
type ChaincodeInvocationSpec struct {
ChaincodeSpec *ChaincodeSpec `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=chaincode_spec,json=chaincodeSpec" json:"chaincode_spec,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
ChaincodeSpec是实际的chaincode的metadata。Type包含java,node等。ChaincodeId在下面有说,ChaincodeInput下面也有说,Timeout是超时时间。
// Carries the chaincode specification. This is the actual metadata required for
// defining a chaincode.
type ChaincodeSpec struct {
Type ChaincodeSpec_Type `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=type,enum=protos.ChaincodeSpec_Type" json:"type,omitempty"`
ChaincodeId *ChaincodeID `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=chaincode_id,json=chaincodeId" json:"chaincode_id,omitempty"`
Input *ChaincodeInput `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=input" json:"input,omitempty"`
Timeout int32 `protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=timeout" json:"timeout,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
ChaincodeID包含Path,Name,Version。
// ChaincodeID contains the path as specified by the deploy transaction
// that created it as well as the hashCode that is generated by the
// system for the path. From the user level (ie, CLI, REST API and so on)
// deploy transaction is expected to provide the path and other requests
// are expected to provide the hashCode. The other value will be ignored.
// Internally, the structure could contain both values. For instance, the
// hashCode will be set when first generated using the path
type ChaincodeID struct {
// deploy transaction will use the path
Path string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=path" json:"path,omitempty"`
// all other requests will use the name (really a hashcode) generated by
// the deploy transaction
Name string `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=name" json:"name,omitempty"`
// user friendly version name for the chaincode
Version string `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=version" json:"version,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
下面来看ChaincodeInput,包含function和arguments,
// Carries the chaincode function and its arguments.
// UnmarshalJSON in transaction.go converts the string-based REST/JSON input to
// the []byte-based current ChaincodeInput structure.
type ChaincodeInput struct {
Args [][]byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=args,proto3" json:"args,omitempty"`
Decorations map[string][]byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=decorations" json:"decorations,omitempty" protobuf_key:"bytes,1,opt,name=key" protobuf_val:"bytes,2,opt,name=value,proto3"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
###### ChaincodeEndorsedAction
// ChaincodeEndorsedAction carries information about the endorsement of a
// specific proposal
type ChaincodeEndorsedAction struct {
// This is the bytes of the ProposalResponsePayload message signed by the
// endorsers. Recall that for the CHAINCODE type, the
// ProposalResponsePayload's extenstion field carries a ChaincodeAction
ProposalResponsePayload []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=proposal_response_payload,json=proposalResponsePayload,proto3" json:"proposal_response_payload,omitempty"`
// The endorsement of the proposal, basically the endorser's signature over
// proposalResponsePayload
Endorsements []*Endorsement `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=endorsements" json:"endorsements,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
// ProposalResponsePayload is the payload of a proposal response. This message
// is the "bridge" between the client's request and the endorser's action in
// response to that request. Concretely, for chaincodes, it contains a hashed
// representation of the proposal (proposalHash) and a representation of the
// chaincode state changes and events inside the extension field.
type ProposalResponsePayload struct {
// Hash of the proposal that triggered this response. The hash is used to
// link a response with its proposal, both for bookeeping purposes on an
// asynchronous system and for security reasons (accountability,
// non-repudiation). The hash usually covers the entire Proposal message
// (byte-by-byte). However this implies that the hash can only be verified
// if the entire proposal message is available when ProposalResponsePayload is
// included in a transaction or stored in the ledger. For confidentiality
// reasons, with chaincodes it might be undesirable to store the proposal
// payload in the ledger. If the type is CHAINCODE, this is handled by
// separating the proposal's header and
// the payload: the header is always hashed in its entirety whereas the
// payload can either be hashed fully, or only its hash may be hashed, or
// nothing from the payload can be hashed. The PayloadVisibility field in the
// Header's extension controls to which extent the proposal payload is
// "visible" in the sense that was just explained.
ProposalHash []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=proposal_hash,json=proposalHash,proto3" json:"proposal_hash,omitempty"`
// Extension should be unmarshaled to a type-specific message. The type of
// the extension in any proposal response depends on the type of the proposal
// that the client selected when the proposal was initially sent out. In
// particular, this information is stored in the type field of a Header. For
// chaincode, it's a ChaincodeAction message
Extension []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=extension,proto3" json:"extension,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
Endorsement包含背书者和签名值。
// An endorsement is a signature of an endorser over a proposal response. By
// producing an endorsement message, an endorser implicitly "approves" that
// proposal response and the actions contained therein. When enough
// endorsements have been collected, a transaction can be generated out of a
// set of proposal responses. Note that this message only contains an identity
// and a signature but no signed payload. This is intentional because
// endorsements are supposed to be collected in a transaction, and they are all
// expected to endorse a single proposal response/action (many endorsements
// over a single proposal response)
type Endorsement struct {
// Identity of the endorser (e.g. its certificate)
Endorser []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=endorser,proto3" json:"endorser,omitempty"`
// Signature of the payload included in ProposalResponse concatenated with
// the endorser's certificate; ie, sign(ProposalResponse.payload + endorser)
Signature []byte `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=signature,proto3" json:"signature,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
BlockMetadata
上面已经分析。
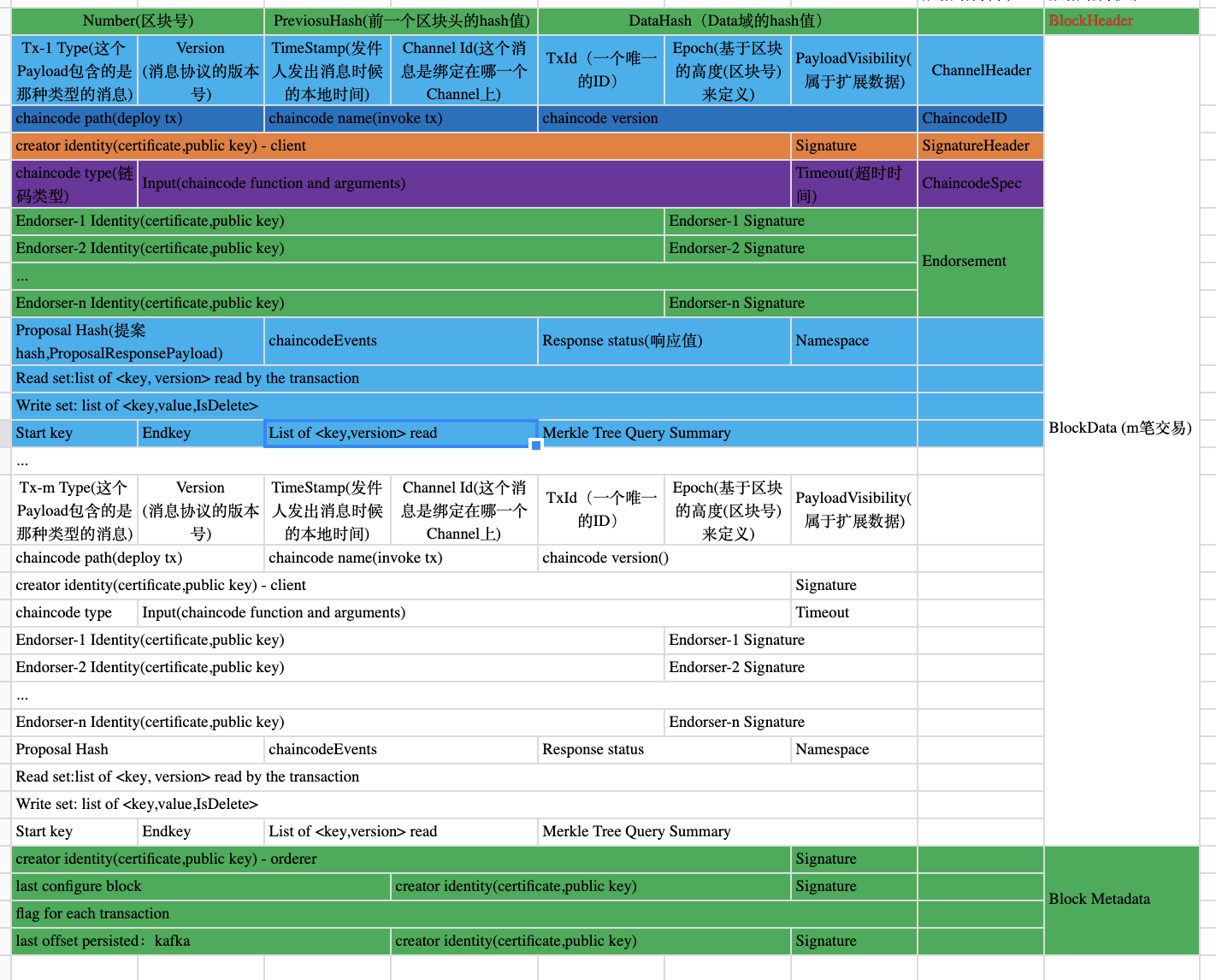
如果想查看高清大图,欢迎关注我的微信公众号「俊语」,回复「区块结构」即可。





