前言
Mysql作为软件开发工程师的必备技能,本人在学习Mysql的过程中遇到了非常多的坑,现在将学习的过程进行记录。
1. 初学Mysql
这里推荐极客时间的《SQL 必知必会》课程。
我基于这个专栏,做了学习笔记,有忘记的语法的话,我会回到这里看下。
2. Java & Mysql
Socket
最早是基于Socket编程来实现的。但是Java和Mysql,Oracle等的规范都不相同。
JDBC
Java Data Base Connectivity,它是可以执行SQL语句的Java API。
为了简化编程和统一各个数据库,进行了抽象。
- 定义了连接(Connection):用来代表和数据库的连接。
- 执行sql语句,用Stagement表示
- 返回的结果用ResultSet表示
public class JDBCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/stu_db/";
// 获取数据库连接
Connection connection = null;
// 获取语句
Statement statement = null;
// 执行结果
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "username", "password");
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from users");
while (resultSet.next()) {
resultSet.getInt("id");
resultSet.getString("name");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
}
}
}
}
上面的个Statement对象是SQL拼接完成的,存在SQL注入的风险,了解下PreparedStatement对象:
- 预编译,提高效率
- 防止SQL注入
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=?");
ps.setInt(1, 10);
JDBCTemplate
上面的那坨代码写着太恶心人了。本质上,数据库访问的操作为:
- 指定数据库连接参数
- 打开数据库连接
- 声明SQL语句
- 预编译并执行SQL语句
- 遍历查询结果
- 处理每一次遍历操作
- 处理抛出的任何异常
- 处理事务
- 关闭数据库连接
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
List<User> users = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from users", new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setName(rs.getString("name"));
user.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
return user;
}
});
并且可以结合Spring进行使用。
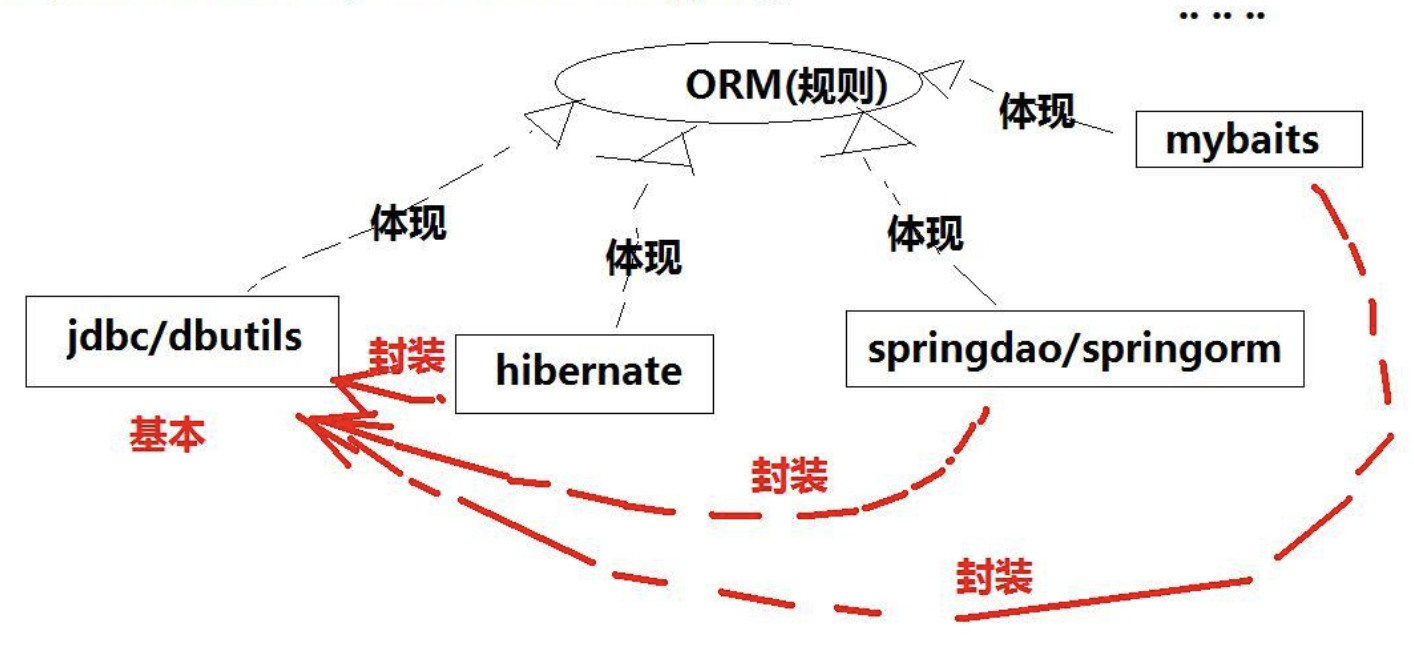
O/R Mapping
O/R Mapping :Object Relational Mapping。
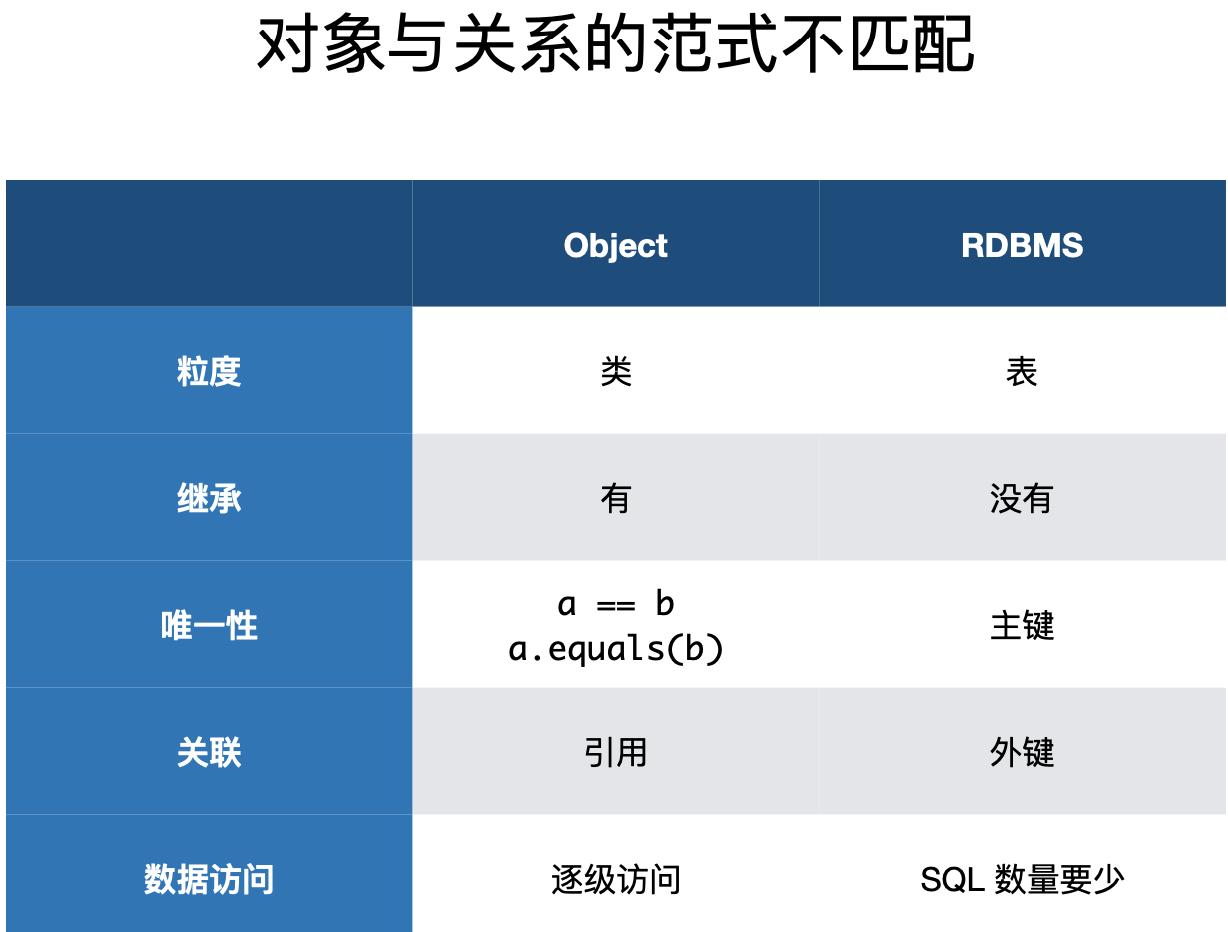
Java对象和Mysql的表数据映射需要我们手动操作,希望把这个过程自动化完成。
JPA
Java Persistence API。
基本的原则:
- 数据库的表和Java的类进行映射
- 表中的行记录和Java对象进行映射
- 表中的列和Java的属性进行映射
涉及到细节
-
很多情况下,多个类合到一起才可以和一张表进行映射,如
public class User { private Name name; private int id; } public class Name { private String firstName; private String middleName; private String lastName; } create table User ( id int not null , firstName VARCHAR , middleName VARCHAR , lastName VARCHAR ) -
Java的类之间有继承关系,Mysql没有
-
对象的标识问题
- Java用a.equals(b)来判断对象是否相等,数据库使用外键
-
对象的关联问题
-
数据导航
- City c = user.getAddress().getCity(); 数据库只能通过表的连接来实现
-
对象的状态
JPA针对这些问题,定义了一系列的规范,Hibernate和Spring Data JPA实现了JPA规范。
| 方式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hibernate | 不再需要编写SQL就可以通过映射关系来操作数据库 | 当多表关联超过3个时Hibermate的级联会损失很多性能;学习成本高 | 适合性能要求不太苛刻的系统,不适合需要大量复杂查询的系统 |
| SpringJDBC | 内嵌Spring框架中、支持AOP;提供了统一的异常处理,框架处理了异常;事务管理 | 只是对原生JDBC进行一层非常薄的封装,没有缓存 | 需要在代码中嵌入SQL语句,适用中小型项目 |
| MyBatis | 满足灵活定制SQL和性能优化的需求 | 编写SQL和映射规则,工作量相对大些 | 性能要求高、响应快、灵活的系统;sql修改、优化比较方便 |
Hibernate
事实上,现有的Hibernate,后有的JPA规范。
Spring Data JPA
使用现有的JPA的实现,进行了简单的封装。
使用demo,可以看到,无需关注SQL编写。
-
配置文件,application.properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true -
Coffee.java
@Entity @Table(name = "T_MENU") @Builder @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Coffee implements Serializable { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String name; @Column @Type(type = "org.jadira.usertype.moneyandcurrency.joda.PersistentMoneyAmount", parameters = {@org.hibernate.annotations.Parameter(name = "currencyCode", value = "CNY")}) private Money price; @Column(updatable = false) @CreationTimestamp private Date createTime; @UpdateTimestamp private Date updateTime; } -
CoffeeOrder.java
@Entity @Table(name = "T_ORDER") @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder public class CoffeeOrder implements Serializable { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String customer; @ManyToMany @JoinTable(name = "T_ORDER_COFFEE") private List<Coffee> items; @Column(nullable = false) private Integer state; @Column(updatable = false) @CreationTimestamp private Date createTime; @UpdateTimestamp private Date updateTime; } -
CoffeeOrderRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository; public interface CoffeeOrderRepository extends CrudRepository<CoffeeOrder, Long> { } -
CoffeeRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository; public interface CoffeeOrderRepository extends CrudRepository<CoffeeOrder, Long> { } -
JpaDemoApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication @EnableJpaRepositories @Slf4j public class JpaDemoApplication implements ApplicationRunner { @Autowired private CoffeeRepository coffeeRepository; @Autowired private CoffeeOrderRepository orderRepository; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(JpaDemoApplication.class, args); } @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { initOrders(); } private void initOrders() { Coffee espresso = Coffee.builder().name("espresso") .price(Money.of(CurrencyUnit.of("CNY"), 20.0)) .build(); coffeeRepository.save(espresso); log.info("Coffee: {}", espresso); Coffee latte = Coffee.builder().name("latte") .price(Money.of(CurrencyUnit.of("CNY"), 30.0)) .build(); coffeeRepository.save(latte); log.info("Coffee: {}", latte); CoffeeOrder order = CoffeeOrder.builder() .customer("Li Lei") .items(Collections.singletonList(espresso)) .state(0) .build(); orderRepository.save(order); log.info("Order: {}", order); order = CoffeeOrder.builder() .customer("Li Lei") .items(Arrays.asList(espresso, latte)) .state(0) .build(); orderRepository.save(order); log.info("Order: {}", order); } }
Mybatis
Mybatis使用
需要关注SQL的编写。
使用Demo:
-
application.properties,配置文件
mybatis.type-handlers-package=geektime.spring.data.mybatisdemo.handler mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true mybatis.mapper-locations = classpath*:mapper/**/*.xml mybatis.type-aliases-package = 类型别名的包名 -
MybatisDemoApplication,MapperScan配置扫描位置
@SpringBootApplication @Slf4j @MapperScan("geektime.spring.data.mybatisdemo.mapper") public class MybatisDemoApplication implements ApplicationRunner { @Autowired private CoffeeMapper coffeeMapper; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MybatisDemoApplication.class, args); } @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { Coffee c = Coffee.builder().name("espresso") .price(Money.of(CurrencyUnit.of("CNY"), 20.0)).build(); int count = coffeeMapper.save(c); log.info("Save {} Coffee: {}", count, c); c = Coffee.builder().name("latte") .price(Money.of(CurrencyUnit.of("CNY"), 25.0)).build(); count = coffeeMapper.save(c); log.info("Save {} Coffee: {}", count, c); c = coffeeMapper.findById(c.getId()); log.info("Find Coffee: {}", c); } } -
Mapper定义接口
@Mapper public interface CoffeeMapper { @Insert("insert into t_coffee (name, price, create_time, update_time)" + "values (#{name}, #{price}, now(), now())") @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true) int save(Coffee coffee); @Select("select * from t_coffee where id = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"), @Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"), // map-underscore-to-camel-case = true 可以实现一样的效果 // @Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"), }) Coffee findById(@Param("id") Long id); } -
Coffee.java
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Builder public class Coffee { private Long id; private String name; private Money price; private Date createTime; private Date updateTime; }
Mybatis原理
MyBatis Generator
可以看到,MyBatis需要我们关注SQL的编写。MyBatis Generator可以根据表帮助我们生成:
- POJO
- Mapper 接⼝
- SQL Map XML
使用:
- 命令行:java -jar mybatis-generator-core-x.x.x.jar -configfile generatorConfig.xml
- mybatis-generator-maven-plugin插件
- mvn mybatis-generator:generate
- ${basedir}/src/main/resources/generatorConfig.xml
MyBatis PageHelper
数据库连接池
HikariCP,Druid。
手动实现一个数据库连接池。
Spring事务管理
在Spring中,事务是我们必须要掌握的。
3. Mysql进阶
Mysql结构
逻辑架构
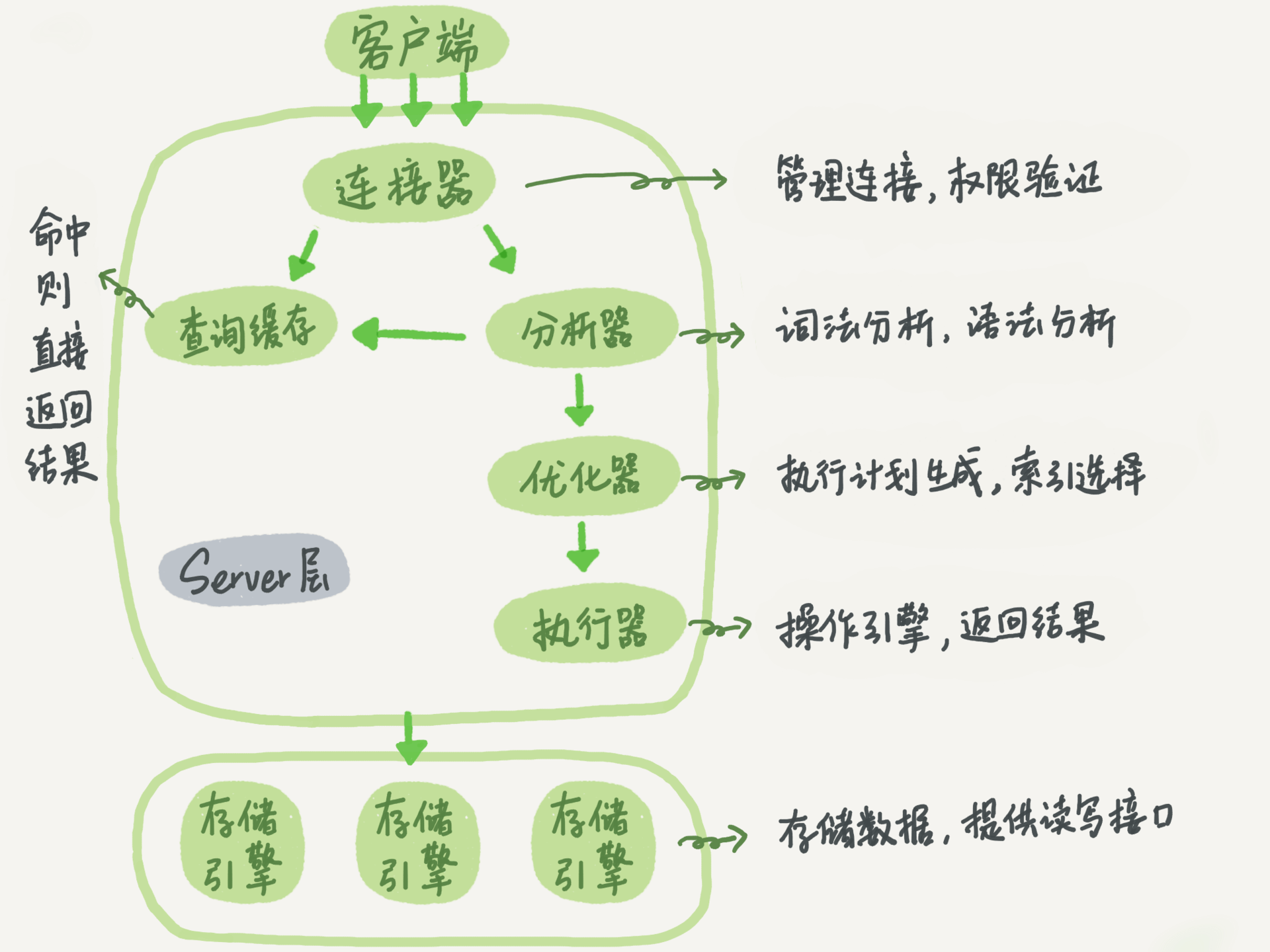
存储引擎
其中,需要关注各个存储引擎的区别。
| 特性 | InnoDB | MyISAM | Memory | Archive |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 存储限制 | 64TB | 256TB | RAM | None |
| 事务支持 | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ |
| 锁粒度 | 行级锁 | 表级锁 | 表级锁 | 行级锁 |
| 支持MVCC | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✔️ |
| 支持B+树索引 | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✖️ |
| 支持哈希索引 | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✔️ | ✖️ |
| 支持全文索引 | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ |
| 支持聚簇索引 | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ |
| 支持外键 | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ |
| 存储成本 | 高 | 低 | N/A(内存) | 非常低 |
| 内存成本 | 高 | 低 | 中等 | 低 |
| 批量插入速度 | 低 | 高 | 高 | 非常高 |
- 如果对事务安全(ACID)要求较高,需要并发控制,或者表上数据更新、删除很频繁,就要选择InnoDB引擎,InnoDB能确保事务完整提交和回滚,并且能有效降低更新、删除操作导致的锁定
- 如果应用主要以插入和查询操作为主,对事务和并发控制没有要求,可以选择MyISAM引擎,MyISAM提供了较高的处理效率
- 如果只是临时存放数据,数据量不大,并且不需要较高的数据安全性,可以选择将数据保存在内存中的Memory引擎,Memory引擎可以提供极快的访问速度。MySQL就使用Memory引擎作为临时表,存放查询的中间结果
- 如果只有插入和查询操作,不要求事务安全,但是对存储成本要求较高,可以选择Archive引擎,Archive支持高并发的插入操作,而且对数据的压缩比很高,适合存储归档数据,例如日志信息
InnoDB核心概念
需要掌握Redo Log,Binlog,(WAL)Write-Ahead Logging和两阶段提交的概念。
这些概念本质上是为了解决:
- 数据更新/插入过程中:高效。
-
系统异常崩溃:数据可恢复
- redolog vs binlog vs undolog
- redolog:重做日志,存储引擎层。记录这一页做了什么改动。
- binlog:归档日志,Server层。2种模式,statement格式是sql语句,row格式是更新前后的数据。
- Undolog:回滚日志,用于多版本并发控制,MVCC
- 两阶段提交(跨系统维持数据逻辑一致性时常用的一个方案)
- redolog用来恢复原库(Mysql异常重启),binlog用来恢复临时库(数据误删除,表扩容)
- WAL
- Write-Ahead Logging,先写日志,在写磁盘。
- Crash-safe
- redo log vs change buffer
- redo log节省的是随机写磁盘的IO消耗,转成了顺序写
- change buffer节省的是随机读磁盘的IO消耗
索引那些事
索引本质上是解决数据快速查找的问题。
需要掌握数据存储的模型,索引的工作原理,常见的索引分类,常见的索引优化技巧。
事务
事务,隔离,MVCC,锁,这些概念之间有什么关系呢?





